World Environment Day 2023: Solutions to Plastic Pollution

5 June 2023 - Today the world is celebrating the World Environment Day, a special day focusing on human efforts to protect, and conserve the global environment. This year the special theme of the Day is #BeatPlasticPollution.
Global cumulative production of plastics since 1950 is forecast to grow from 9.2 billion tons in 2017 to 34 billion tons by 2050 (Geyer, 2020). Therefore, plastic pollution definitely represents a highly important environmental, economic, and social topic globally, and for the Baltic Sea region in particular.
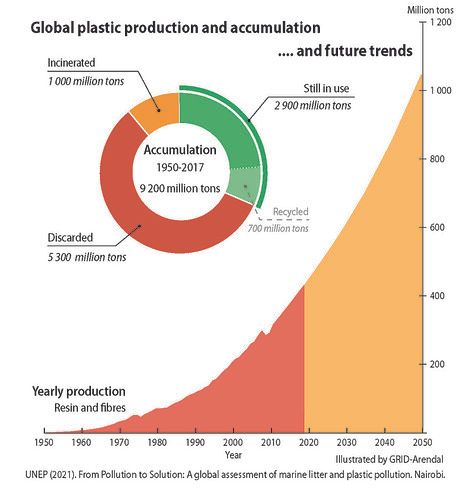
Credit & original image: GRID-Arendal
It is estimated that 75 to 199 million tonnes of plastic is currently found in our oceans. Unless we implement drastical changes in our approach to plastic production, usage and disposal, the amount of plastic waste entering aquatic ecosystems could nearly triple from 9-14 million tonnes per year in 2016 to a projected 23-37 million tonnes per year by 2040. How does it get there? A lot of it comes from the world's rivers, which serve as direct conduits of trash into lakes, seas, and the ocean.
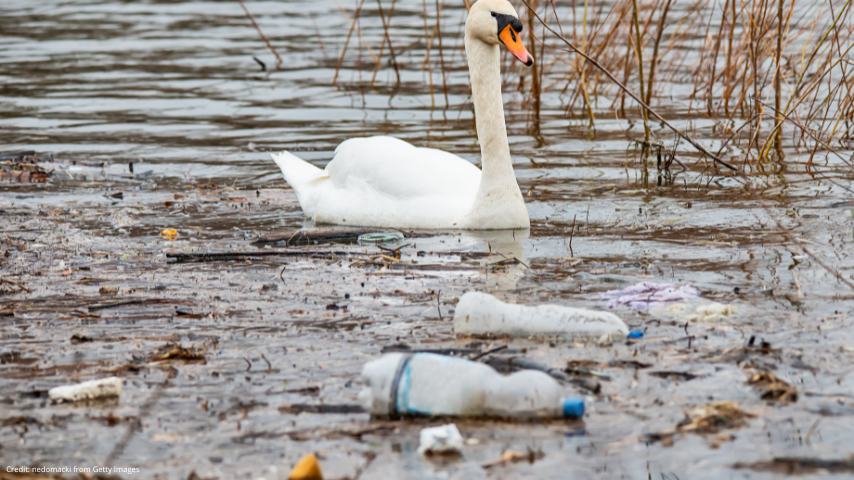

Plastic and impacts on marine ecosystems
Ingestion, physical entanglement, smothering, and the transport of pathogens in biofilms are causing a range of lethal and non-lethal effects in marine organisms, including physiological disturbances, disease, changes in gene expression, alterations of behaviour, and shifts in species assemblages and biodiversity. These in turn, have impacts on ecosystems, leading to a wide range of social and economic consequences such as loss of revenue from natural resources and damage to maritime industries and coastal infrastructure.
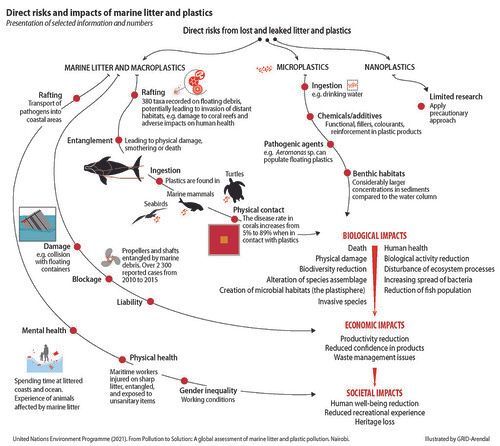
Credit & original image: GRID-Arendal
Marine microplastics: example of plastic impact on marine environment
Plastic pollution has led (among other things) to microplastic contamination of the whole marine environment, from the shore to the deepest ocean sediments (e.g. Ryan et al. 2009; Woodall et al. 2014). These microplastic particles can adsorb and transport contaminants from the surrounding environment, adding to the many chemical additives that are incorporated during the production of the plastic. Marine organisms can ingest this plastic directly, or by consuming other organisms that contain plastic.
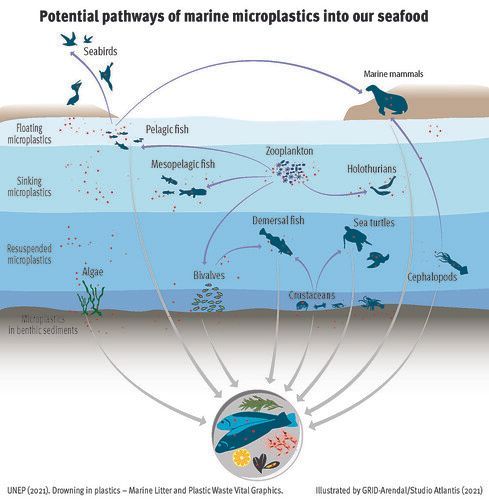
Credit & original image: GRID-Arendal/Studio Atlantis
How CCB is working on plastic?
CCB and its member organizations have been working for many years to address the issue of plastic pollution in the Baltic Sea region in frame of it Hazardous Substances and Marine Litter Working area. Examples of our activities include the projects Plastic Free Baltic, Plastic Free Ocean, and the “#NonHazPlasticDiet” campaign.
Our current thematic plastic engagements include CCB participation in the EU Interreg project “Baltic Approaches to Handling Plastic Pollution under a Circular Economy Context” - BALTIPLAST (2023-2025). The project aims at the prevention and reduction of plastic waste in the Baltic Sea Region, focusing on single use plastic reduction, improvements in plastic packaging and innovative collection and treatment systems at the municipality level.
Soon this year, CCB will release the new report "Keep Fibers Zipped", which will cover available solutions to tackle microfiber pollution from textile in the Baltic Sea region, and globally.
***
Article written by Eugeniy Lobanov, CCB Hazardous Substances Working Area Leader
EXTRA RESOURCES
- For the World Environment Day, the UNEP has prepared an interactive multi-language visual guide under the title: Our planet is choking on plastic. aims at the prevention and reduction of plastic waste in the Baltic Sea Region, focusing on single use plastic reduction, improvements in plastic packaging and innovative collection and treatment systems at the municipality level. Also, a UNEP-developed Practical Guide “Beat Plastic Pollution” is available for everyone.
- Forever Toxic: The science on health threats from plastic recycling. May, 2023. The report has been prepared by Greenpeace, USA in collaboration with International Pollutants Elimination Network (IPEN) and The Last Beach Cleanup.
- UNEP report: From Pollution to Solution: a global assessment of marine litter and plastic pollution and associated Interactive Story: From Pollution to Solution.
- Break Free From Plastic – the global movement envisioning a future free from plastic pollution.


