Plastics Treaty negotiations: we need higher ambition

Nairobi, Kenya – The third meeting of the Intergovernmental Negotiating Committee (INC-3) for a global agreement to end plastic pollution concluded on 19th of November at the UNEP headquarters in Nairobi. Despite a mandate for a revised draft, Member States failed to reach an agreement on priorities for intersessional work ahead of INC-4, despite an 11th-hour attempt, jeopardizing significant advancements for the treaty process.
With the significant petrochemical influence in the treaty negotiations, including the ‘low ambition’ of a group of ‘like-minded’ plastic-producing countries, and the lack of ambition by the so-called ‘high ambition’ countries, the INC-3 concluded without concrete headway towards the mandate adopted at the fifth United Nations Environment Assembly (UNEA 5.2) to negotiate a comprehensive and legally binding treaty that will cover measures along the entire life cycle of plastic.
Downstream actions are not enough
According to the views of many Member States and INC observers, and based on mandate of UNEA resolution 5/14, a strong Global Plastics Treaty shall take into account the entire life cycle of plastics, from production to disposal. The most comprehensive modeling, incorporating the recent report “Towards Ending Plastic Pollution: 15 Global Policy Interventions for Systems Change” by Systemiq/the Nordic Council of Ministers, indicates that effectively tackling plastic pollution throughout its life cycle necessitates the implementation of supply-side controls on plastic production. Given the absence of projections indicating that waste management capacity will ever align with current estimates of plastic production, reducing the supply is the sole viable long-term solution. Currently, less than 10% of plastic waste is recycled, the U.N. Environment Programme says, while at least 14 million tonnes end up in oceans every year, the International Union for Conservation of Nature says.

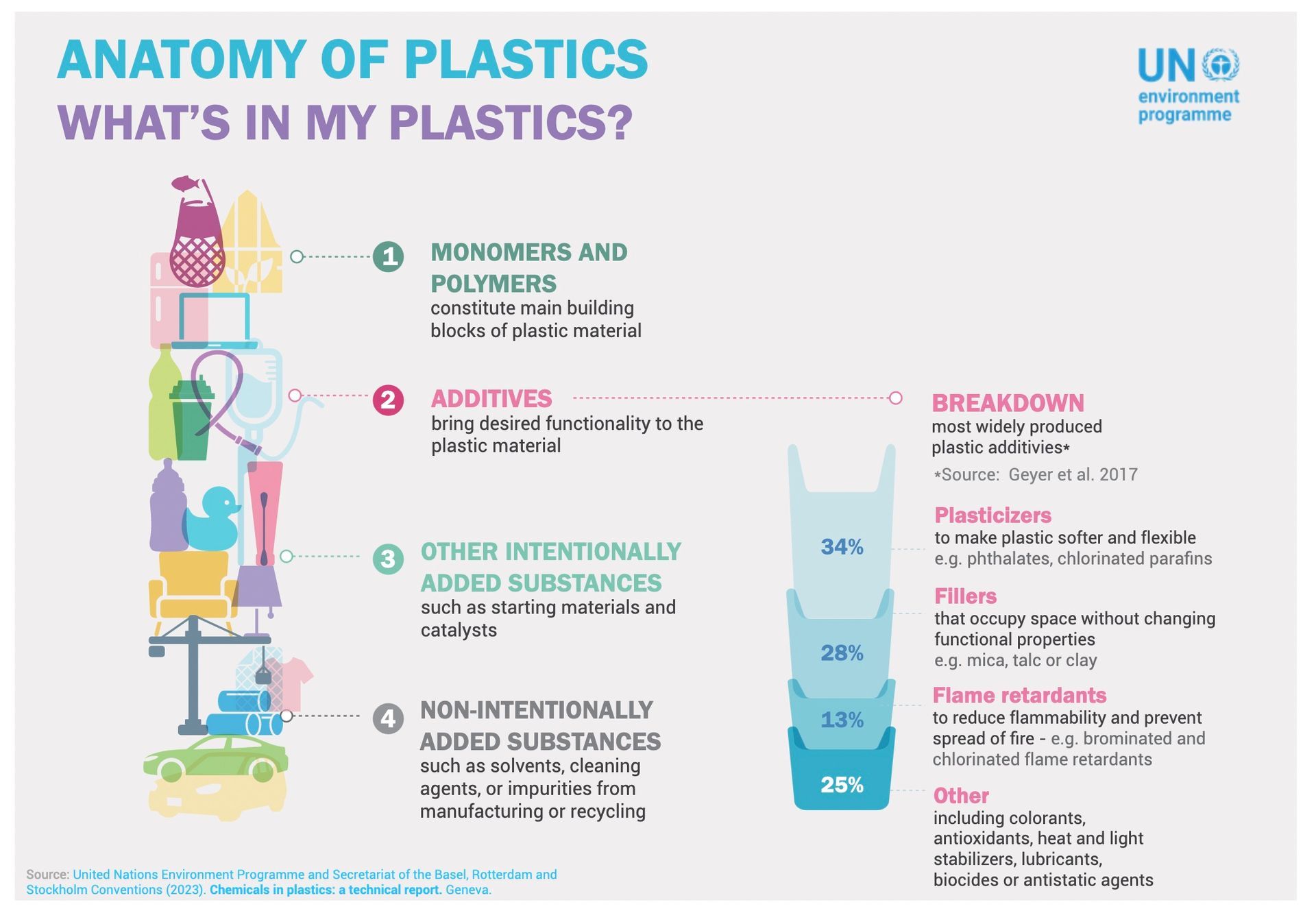
Chemicals in plastics
During the negotiations many countries strongly supported provisions on addressing chemicals of concern, and protecting human and environmental health from chemicals in plastics.
A proposal by Switzerland and Uruguay to hold more discussions on curbing harmful polymers and chemicals of concern garnered support from more than 100 members states. It was an expectation from many Member States and observers, that INC will mandate intersessional work to create an initial list of chemicals of concern, including monomers and polymers, to be listed in the Annexes of the Treaty, together with respective criteria for their selection. However, the influence of a group of other countries, including fossil fuel and plastic-producing countries overpowered these perspectives.
CCB along with many other environmental organizations, including
IPEN reminds that plastics are a combination of chemicals and carbon. Thousands of those chemicals are known to be chemicals of concern and for most of the rest there is a remarkable lack of data. Moreover, for users and the waste management sector there is limited, or in most cases no data on the chemical composition of plastic materials and products. This lack of transparency, traceability, and available data means that there are no plastics that can be considered safe, since it is not possible to know if they contain toxic chemicals. These gaps are also key obstacles toward a safe circular economy.
Unfortunately, after seven days of negotiations, the INC-3 missed the opportunity to set the stage for ambitious intersessional work on any priority, including the development of targets, baselines, and schedules for an overall reduction in plastic production, as well as strict reporting mechanisms to inform and monitor compliance with a global reduction target.

“Currently, we see a lack of clear path towards to an effective Plastic Treaty. And there is a clear division between different Member States regarding the level of ambitious, and even scope of the upcoming Treaty. We really need to address this political divide very soon, as we have only 2 more rounds of talks in 2024”, commented Eugeniy Lobanov, CCB Hazardous Substances and Marine Litter Working Area Leader, and participant at the INC3.
The week in detail
Most of the INC-3 week was spent in three contact groups: (1) Contact group 1 reviewed the first two parts of the Zero Draft: Part I (Preamble, objective, definitions, principles, and scope) and Part II (Primary plastic polymers, chemicals and polymers of concerns, problematic and avoidable plastics, exertions, product design -including reuse-, substitutes, extended producer responsibility, emissions, waste management, trade, existing plastic pollution, just transition, and transparency). (2) Contact group 2 focused on the second two parts: Part III (financing and capacity building), and Part IV (National plans, implementation and compliance, reporting, and monitoring). (3) Contact group 3 discussed the Synthesis Report containing elements not discussed at previous meetings and intersessional work.
During the week, civil society organizations exposed the conflict of interest within the INC-3 process, starting with the publication of an analysis of the participants revealing that 143 fossil fuel and chemical industry lobbyists registered for INC-3, a 36% increase from INC-2; some of whom were registered under six Member States delegations.
The INC-3 agreed that the next round of negotiations (INC-4) will be held in Ottawa, Canada, on 21 - 30 April 2024, and INC-5 in Busan, Republic of Korea on 25 November to 1 December 2024. Ambassador Luis Vayas Valdiviezo (Ecuador) was confirmed as Chair for the rest of the INC process.
***
Article written by Eugeniy Lobanov, CCB Hazardous Substances Working Area Leader
Resources:
UNEP online resource page for INC-3

